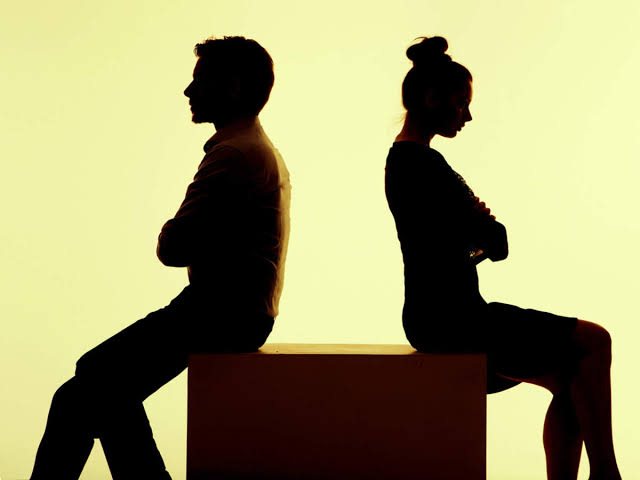
ಬೆಂಗಳೂರು: ಇತ್ತೀಚಿನ ದಿನಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಮದುವೆ ಸಂಬಂಧ ಮುರಿದು ಬೀಳುವುದು ಮಾಮೂಲು ಎನ್ನುವಂತೆ ಆಗಿದೆ. ಸಣ್ಣಪುಟ್ಟ ವಿಚಾರಕ್ಕೂ ಡಿವೋರ್ಸ್ ಕೇಳುತ್ತಾರೆ ಹುಡುಗಿಯರು ಅನ್ನೋ ಕಂಪ್ಲೇಂಟ್ ಮಾಡುತ್ತಾರೆ ಹುಡುಗರು. ಅದೇ ರೀತಿ, ಇದೀಗ 7.8 ಕೋಟಿ ರೂಪಾಯಿಗೂ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಸಂಬಳ ತರುವ ಗಂಡನ ಬಳಿ ಹೆಂಡತಿ ಡಿವೋರ್ಸ್ ಕೇಳುತ್ತಿದ್ದಾಳಂತೆ.
ಸೋಷಿಯಲ್ ಮೀಡಿಯಾದಲ್ಲಿ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯೊಬ್ಬನ ಪೋಸ್ಟ್ ವೈರಲ್ ಆಗುತ್ತಿದ್ದು, ಈ ಪೋಸ್ಟ್ ನೋಡಿ ಜನ ಬೆಚ್ಚಿಬಿದ್ದಿದ್ದಾರೆ. ಅಷ್ಟಕ್ಕೂ ಈ ಸ್ಪೆಷಲ್ ಪೋಸ್ಟ್ ಒಳಗೆ ಇರುವುದು ಏನಪ್ಪ ಅಂದ್ರೆ, ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ನಾನು ದಿನಕ್ಕೆ 14 ಗಂಟೆ ಕೆಲಸ ಮಾಡುತ್ತೇನೆ ಮತ್ತು ನನಗೆ ಇದೀಗ 7.8 ಕೋಟಿಗೂ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಸಂಬಳ ಕೊಡುತ್ತಿದ್ದಾರೆ. ಆದರೆ ನನ್ನ ಹೆಂಡತಿ ಇದೀಗ ಡಿವೋರ್ಸ್ ಕೇಳುತ್ತಿದ್ದಾಳೆ ಎಂದು ಬರೆದುಕೊಂಡಿದ್ದಾರೆ.
ಇದಕ್ಕೆ ಉತ್ತರ ನೀಡಿರುವ ನೆಟ್ಟಿಗರು, ನೀವು ಯಾವಾಗಲೂ ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ಉದ್ಯೋಗಿಯಾಗೇ ಬದುಕಿ. ಟಾಪ್ ಆಗಿ ಬಂದರೆ ನಿಮ್ಮ ಸಂಸಾರ ನೆಟ್ಟಗೆ ಇರಲ್ಲ, ನಾನು ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ಉದ್ಯೋಗಿ ಆದರೆ ಜೀವನದಲ್ಲಿ ನೆಮ್ಮದಿಯಾಗಿ ಇದ್ದೇನೆ ಅಂತಾ ಕಾಲು ಎಳೆದಿದ್ದಾರೆ. ಇದರ ಜೊತೆಗೆ, ಇನ್ನೂ ಕೆಲವರು ಸಂಸಾರ ಉಳಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಲು ಈಗ ಇರುವ ಅವಕಾಶಗಳ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಸಲಹೆ ನೀಡಿ ಹಲ್ಚಲ್ ಎಬ್ಬಿಸಿದ್ದಾರೆ.